Introduction:
The concept of the metaverse has evolved from science fiction to a tangible digital reality. As more people dive into this immersive digital space, the demand for advanced tools and equipment has surged. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the essential tools and equipment used in the metaverse, providing insights into how these technologies are shaping the way we interact, create, and experience this emerging digital frontier.
Metaverse Tools and Equipment
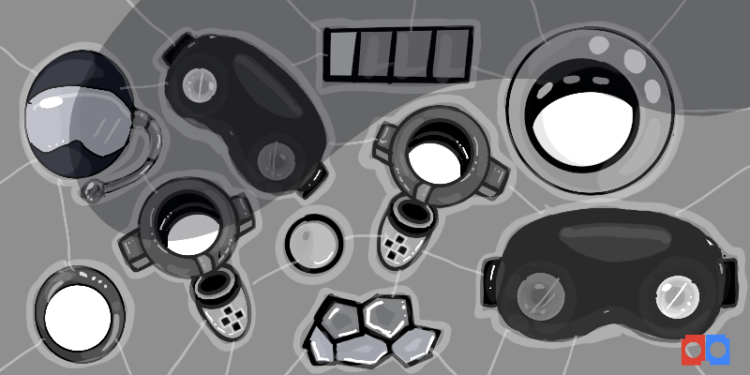
I. Virtual Reality (VR) Headsets:
At the forefront of the metaverse experience are virtual reality (VR) headsets. These devices transport users into a three-dimensional, computer-generated environment, allowing for unparalleled immersion. As of 2024, several cutting-edge VR headsets have gained popularity, such as the Oculus Quest 2, HTC Vive Pro 2, and the Valve Index.
a. Oculus Quest 2:
The Oculus Quest 2, developed by Meta (formerly Facebook), is a standalone VR headset that has taken the metaverse by storm. With its wireless capabilities, high-resolution display, and vast library of VR content, it has become a staple for both casual users and professionals.
b. HTC Vive Pro 2:
The HTC Vive Pro 2 offers an exceptional VR experience with its high-resolution display, precise tracking, and comfortable design. Designed with gamers and content creators in mind, it provides a platform for diverse metaverse activities, from gaming to virtual collaboration.
c. Valve Index:
Valve Index stands out with its advanced tracking system and high-fidelity audio. It’s a favorite among enthusiasts who prioritize precision and realism in their metaverse interactions. With its finger-tracking controllers, the Valve Index adds an extra layer of immersion to virtual experiences.
II. Augmented Reality (AR) Devices:
While VR headsets immerse users in a completely virtual environment, augmented reality (AR) devices overlay digital content onto the real world. AR technology has found its way into various tools and equipment, enhancing our perception and interaction with the metaverse.
a. Microsoft HoloLens 2:
Microsoft HoloLens 2 is a leading AR headset that blends the virtual and physical worlds seamlessly. It’s equipped with sensors, hand-tracking capabilities, and a high-resolution display, making it a versatile tool for professionals in fields like design, healthcare, and education.
b. Magic Leap One:
Magic Leap One is another AR headset that aims to merge the digital and physical realms. With its lightweight design and spatial computing technology, Magic Leap One enables users to interact with digital content as if it were part of the real world, opening up innovative possibilities for metaverse experiences.
III. Haptic Feedback Devices:
One of the challenges in creating a truly immersive metaverse experience is replicating the sense of touch. Haptic feedback devices address this challenge by providing tactile sensations to users, enhancing their overall immersion and interaction with virtual environments.a. Haptic Gloves:
Haptic gloves are designed to simulate the sensation of touch by providing feedback to the user’s hands. These gloves use sensors and actuators to convey a sense of texture, pressure, and resistance, allowing users to feel and manipulate virtual objects.
b.Haptic Vests:
Haptic vests extend the immersive experience beyond the hands by providing tactile feedback to the entire upper body. These vests use a combination of vibrational motors and sensors to simulate sensations like impact, vibration, and even environmental conditions, enhancing the overall metaverse experience.
IV. Motion Tracking Systems:
For a metaverse experience that mirrors real-world movement, motion tracking systems play a crucial role. These systems capture the user’s movements and translate them into the virtual environment, enabling a more natural and intuitive interaction.
a. Lighthouse Tracking (used in HTC Vive):
Lighthouse tracking, employed by the HTC Vive series, uses external sensors to track the precise position of VR devices and controllers. This technology allows for a large play area and accurate motion tracking, contributing to a more immersive metaverse experience.
b. Inside-Out Tracking (Used in Oculus Quest 2):
Inside-out tracking, as seen in the Oculus Quest 2, eliminates the need for external sensors by utilizing built-in cameras on the VR headset. This technology enables users to move freely in virtual spaces without the constraints of external hardware, promoting ease of use and accessibility.
V. Virtual Collaboration Tools:
The metaverse is not just about entertainment; it’s also becoming a hub for virtual collaboration and communication. As remote work becomes more prevalent, these tools are essential for connecting individuals across the digital landscape.
a. Spatial:
Spatial is a virtual collaboration platform that transforms traditional video meetings into immersive 3D spaces. Users can interact with digital content, share ideas, and collaborate seamlessly, making it an invaluable tool for remote teams and professionals seeking a virtual office experience.
b. VirBELA:
VirBELA offers a virtual world for team collaboration, conferences, and events. With customizable environments, spatial audio, and avatars, VirBELA provides a dynamic space for networking, presentations, and collaborative work within the metaverse.
VI. Blockchain and NFTs:
The metaverse is not only a space for digital experiences but also a platform for digital ownership. Blockchain technology and non-fungible tokens (NFTs) play a significant role in establishing ownership and authenticity of digital assets within the metaverse.
a. Decentraland:
Decentraland is a virtual world built on blockchain technology where users can buy, sell, and build on virtual land. The ownership of virtual real estate is secured through blockchain, and users can monetize their creations or experiences using cryptocurrency.
b. Crypto Art Platforms:
NFTs have revolutionized the art world, allowing artists to tokenize their work and sell digital assets with provable ownership. Platforms like OpenSea and Rarible enable artists to showcase and sell their digital creations within the metaverse, creating new opportunities for the intersection of art and technology.
Conclusion:
The metaverse is rapidly evolving, and the tools and equipment mentioned here represent just a glimpse of the technological landscape shaping this digital frontier. As virtual and augmented reality continue to advance and blockchain technology transforms digital ownership, the metaverse is poised to become an integral part of our daily lives.
Whether you’re a gamer, a professional exploring virtual collaboration, or an artist venturing into the world of digital creation, understanding and embracing these tools will empower you to navigate and thrive in the exciting realms of the metaverse. Stay tuned as innovations unfold, blurring the lines between the physical and the digital and ushering in a new era of immersive experiences.